class a foam acts as a surfactant which means that it
This is a biodegradable mixture of. As a carbon-loving solution Class A foam soaks into solid combustible materials by breaking down the surface tension of the water.
The ability for surfactants to stabilise the liquid-gas interface prevent bubble rupture and allow foam formation is due to their amphphillic nature.

. It helps the water penetrate the burning. The energy need to increase the surface area A is γδAδt so a low γ means more foam for less energy. The negative charge helps the surfactant molecules lift and suspend soils in.
Class A foam is for use against Class A fires such as paper rubber textiles and wood. This is nothing to do with. Class A Foam is specially formulated to make water more effective for firefighting.
The pressure inside a foam of radius R that contributes to its self-destruction is 2γR. They are molecules that are possess a. There are surfactants in Class A foam that allow the water to penetrate the burning fuels quickly by greatly reducing water surface tension.
Anionic surfactants have a negative charge on their hydrophilic end. What is class A foam made of. A foaming agent is a material that facilitates the formation of foam such as a surfactant or a blowing agent.
Because Class A foam acts as a surfactant when mixed with water its able to more effectively penetrate deep-seated fires including fires within mattresses sofas vehicle. Class A foam is used on common combustibles such as paper wood and textiles. Suppressing - Foams especially Class A are extremely effective at allowing water to penetrate into the fuel upon which it is applied either absorbing heat or generating a film.
Surfactants allow the water to go further and soak. These surfactants are selected for their 2 main properties. Class A foams are mainly made of synthetic surfactants.
The surfactants in Class A foam significantly reduce waters surface tension and when mixed with. Class A foams are often intended for use at very low concentration of 01 to 1 and are. Class B foam is used on flammable liquids.
The second reason that surfactants help create foam is that the liquid in the foam walls is naturally sucked out of the walls into the edges. A surfactant when present in small amounts reduces surface tension of a.

How Does A Fire Fighting Foam Concentrate Work On Fire Bioex

A Review Of Shampoo Surfactant Technology Consumer Benefits Raw Materials And Recent Developments Cornwell 2018 International Journal Of Cosmetic Science Wiley Online Library
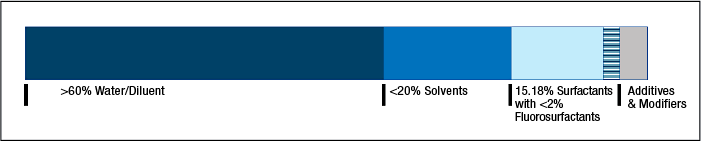
3 Firefighting Foams Pfas Per And Polyfluoroalkyl Substances
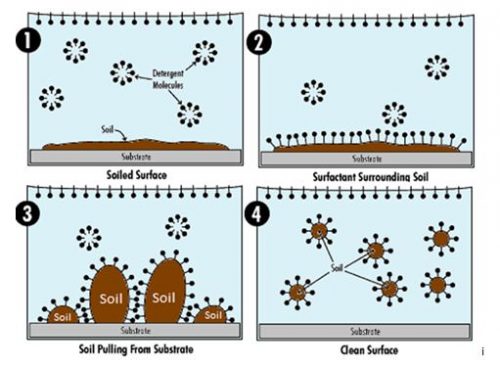
An Easy Guide To Understanding How Surfactants Work Ipc

Compatibility Of Aqueous Film Forming Foams Afff With Sea Water Sciencedirect

Foamability Of Aqueous Solutions Role Of Surfactant Type And Concentration Sciencedirect

Use Of Foam On Class A Fire Bioex

Foamability Of Aqueous Solutions Role Of Surfactant Type And Concentration Sciencedirect

Surfactant Definition Properties Examples Facts Britannica

Use Of Foam On Class A Fire Bioex

Naval Research Lab Chemists Search For Pfas Free Firefighting Foam U S Department Of Defense Defense Department News

Essential Factor Of Perfluoroalkyl Surfactants Contributing To Efficacy In Firefighting Foams Langmuir
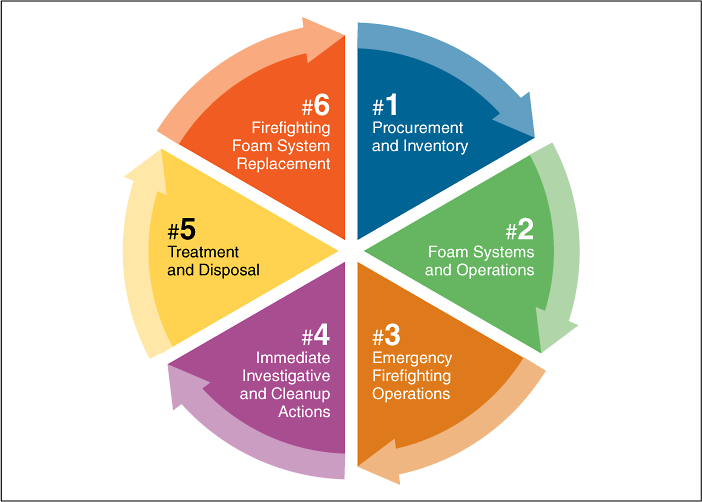
3 Firefighting Foams Pfas Per And Polyfluoroalkyl Substances

Surface Active Agents Surfactants Types And Applications
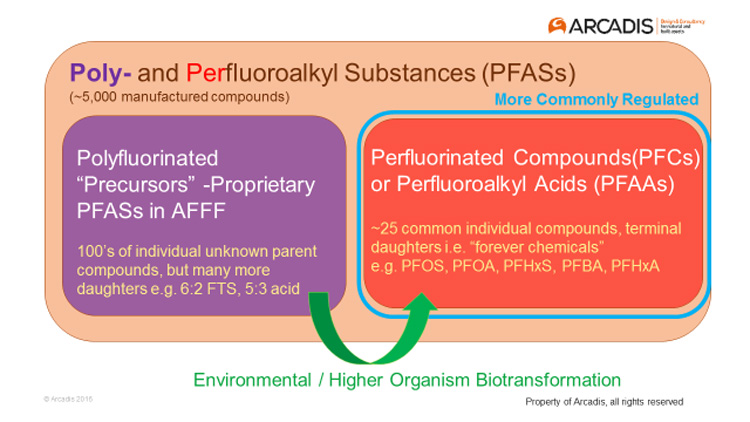
Is The Downfall Of Afff A Precursor To Long Term Environmental Liabilities

The Role Of Surfactant Structure On Foam Behaviour Sciencedirect


